Overview

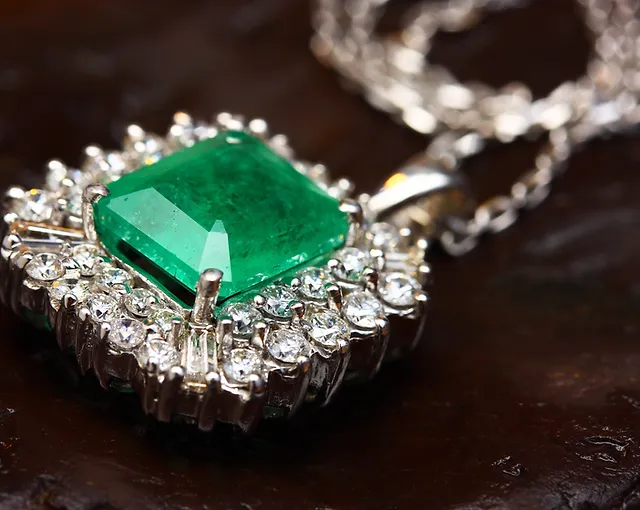
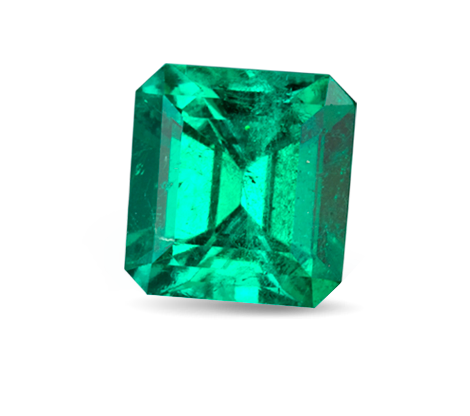
About Emerald
Beloved by the Egyptian Queen Cleopatra, Emerald is a precious gemstone made from a variety of the mineral called beryl. Chromium is the trace element responsible for emerald’s vibrant green. Deriving from the ancient Greek word for green, “Smaragdus”, it is often associated with lush landscapes and represent new spring growth. Wearing an emerald was believed to reveal the truth or falseness of a lover’s oath as well as make one an eloquent speaker.
Emerald Properties
Mineral: Beryl
Chemistry: Beryllium Aluminum Silicate (Be3Al2Si6O18)
Refractive Index: 1.570 – 1.599
Birefringence: 0.005 to 0.010
Specific Gravity: 2.72
Mohs Hardness:8.0

Main Colour
Green
Other Colours
Greenish Blue
Yellowish Green
Common Shapes




Birthstone Month
May
Treatments / Enhancements
Oiling Treatment and/or Artificial Resin is usually used to improve colour and clarity
Similar Gemstones
Aquamarine, Morganite, Peridot
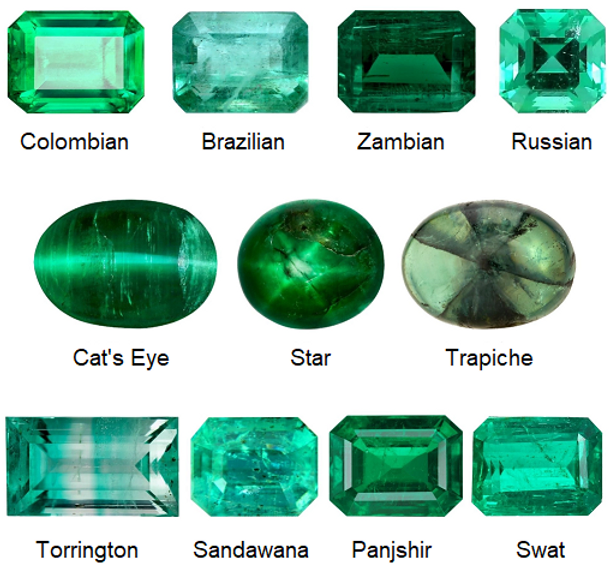
Origins
Afghanistan, Madagascar, Brazil, Colombia, Ethiopia, Pakistan, Russia, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Colour
Colour is the most significant factor affecting the value of an emerald.
Colour preferences do change in time and from culture to culture. Nevertheless, the most sought after colour is bluish green to pure green, with vivid colour saturation and tone that’s not too dark. Highly transparent, evenly distributed colour with no visible colour zoning are the most valued emeralds. The value of an emerald decreases if the colour tone of the gem is either too yellowish or too blueish as it will be consider as a beryl variety instead of an emerald.

Emeralds with 3 different undertones
Colour Grades of Emeralds
Emeralds not only have different colour/undertone shades, they also come shades of green with varying intensity as well. Below is some of the Emeralds with different shade intensity.
Deep

Vivid

Intense

Medium

Light

Colour Intensity
Intensity of the green within emeralds differs depending on the presence of elements and mining locations. This is due to the difference in the amount of chromium, vanadium and iron. This elements are the main reason for the colour within emeralds. The presence and absence of the is the determining factor for the gems exact colour.
Emeralds mined from different locations have different colour intensity as well. Colombian mined emeralds have a warmer and more intense pure green colour. Zambian emeralds have a cooler, more bluish green colour. However, Emerald appearances overlap between all the mining sources.
Clarity
Clarity of a gem is judged based off the gem’s opacity and how much inclusions does the gem contain. The assessment of clarity is often done thru eye clean and it follow the same grading as with diamonds. Inclusions within the gem affects the value of the gem. The more visible the inclusions are to the visible eye, the lower the value of the gem.

Emeralds with 3 different opacity
Emeralds typically expected to contain inclusions, because inclusion-free emeralds are practically nonexistent. Value of the emerald depends on how visible the inclusions are. Obvious inclusions, or inclusions that reduce transparency or brightness, lower a emerald’s value drastically. The most common types of inclusions found in emeralds are moss-like inclusions called Jardin.
Clarity Grades of Emeralds
Clarity in transparent emeralds is assessed by naked eye only and at distance of about 40cm. Emeralds are classified as type 3 stones. This means that they will almost always have inclusions that are visible to the naked eye. Traders and consumers understand this and therefore it is accepted.
Jardin
Inclusions within emeralds are often mossy and garden-like. They are often referred to as “Jardin”, the french word for garden. They are a mix for solid, liquid and gas within the gem itself. It appears light green and whitish in colour
Completely transparent emeralds are assumed to be either unnatural or undergone heavy treatment until tested, because it is extremely rare to find transparent emeralds in nature. Jardin helps the gemologist determine whether the gem is natural gem, synthetic gem or an imitation. It also help to determine the location of where the gem originated from.

Cut
The shape of the emerald crystal influences the finished stone’s shape and size. Gem cutters have to consider the emerald rough’s depth of colour, durability, and inclusions when making cutting decisions. This is to minimize the weight loss from the cutting as it will affect the value of the final gem.
Emerald Fractures
Emerald rough contains significant fractures within it. This affect the decision making of the gem cutters. They have to cut it in such a way that the fracture will not affect the finished gem.
Not only that, there can also be inherent fractures. As emeralds are more brittle than corundum, it makes the gem more vulnerable during cutting and even daily wear. The cutter also have to make decisions to reduce the possibility of this type of fractures from happening. Vulnerable areas are faceted in a way to provide safe areas for the prongs.
Dichroism
Instead of exhibiting pleochroism like most gemstones, emerald mainly exhibit blueish green and yellowish green dichroism. This encourages the table orientation to favour perpendicular to the crystal’s length, which will let the cutter achieve the more coveted blueish green shade.
Colombian emerald roughs are harder to cut due to the fact that the colour is concentrated to the surface of the crystal. if not careful, the resulting colour might be lighter than normal. This will also affect the number of facets the crystal will have as the cutter will want to maximise the crystal’s hue, saturation and tone.
Carat
Gemstones such as Emeralds are denser than diamonds, therefore the carat weight for a gemstones differs from that of a diamond. Size of gemstones, including emeralds, are measured by carat as well as their diameter in millimeters. However, Emeralds are more valued for their colour, cut and clarity.
Emeralds have a wide size range from a few points to hundreds of carats. There are emeralds in museums and private collections that weigh hundreds of carats. At the other extreme are tiny emeralds that weigh fractions of a carat. Most emeralds weigh less than 1.5 carats because larger stones are rare. The larger the size, the more expensive the gemstone.