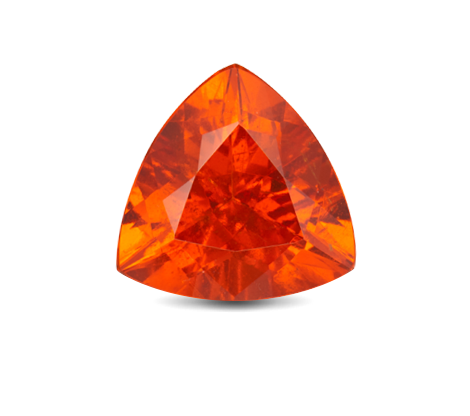
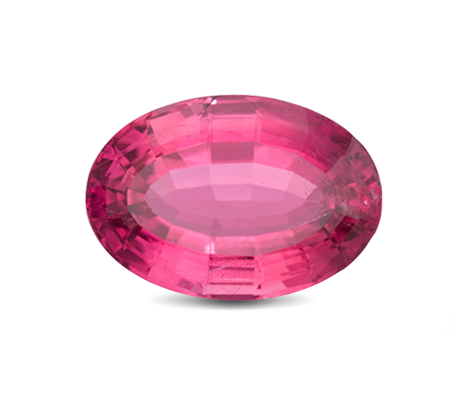
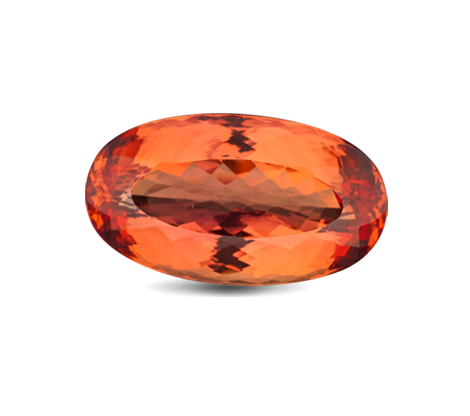
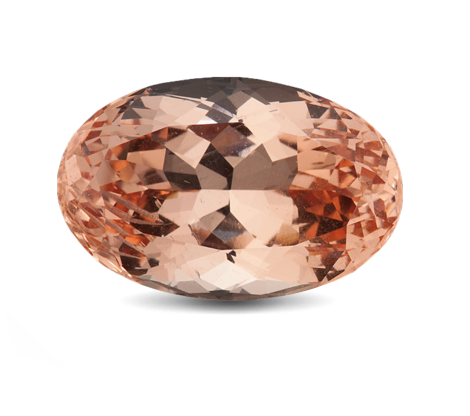
Overview
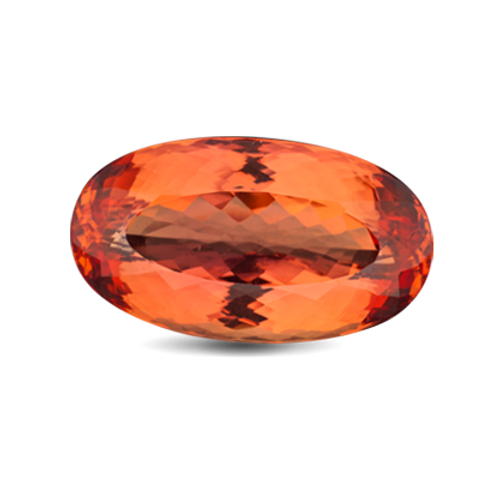

About Topaz
Having its name derived from the Sanskrit word for fire and the Greek name of Topazios. Believed to give its wearer strength, beauty, intelligence, this gem consist of a wide range of colour shades. Thought to dispel anger and break magic spells, this gem has been used by royalty and rival other gems such as pink sapphires.
Topaz Properties
Mineral: Topaz
Chemistry: Aluminium Silicate with Fluorine (Al2(F,OH)2SiO4)
Refractive Index: 1.619 – 1.627
Birefringence: 0.008 to 0.010
Specific Gravity:3.53
Mohs Hardness:8.0
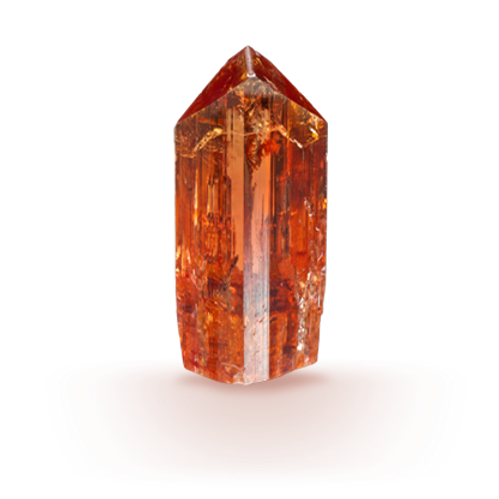

Colours in Incandescent Light
Orange
Blue
Other Colours
Yellow
Brown
Purplish Pink
Common Shapes




Birthstone Month
November, December
Treatments / Enhancements
Heat Treatment is usually used to improve colour and clarity
Similar Gemstones
Origins
United States, Madagascar, Brazil, Russia, Pakistan, Mexico
Colour
Colour is the most significant factor affecting the value of a topaz.
Colour preferences do change in time and from culture to culture. Nevertheless, the most sought after colour is red topaz with vivid colour saturation. Highly transparent, evenly distributed colour with no visible colour zoning are the most valued topaz. The value of a topaz changes according to what colour the gem itself has, with red being the most highly prized.

Topaz with its different colours
Colour Grades of Topaz
Topaz not only have different colour/undertone shades, each of those shades come with varying intensity as well. Below is some of the topaz with different shade intensity.

Blue Topaz with different intensities

Yellow Topaz with different intensities
Colours of the Topaz
With large range of colour hues, there has to be a ways to differentiate between the shades. Different shades of Topaz have different trade names based off the colours and treatments the gems underwent.
Imperial Topaz
For Topaz that contain Red hues, they are referred to as Imperial Topaz. They are the most highly prized and coveted due to its rarity. it is insisted that the gem must display a reddish pleochroic colour in order to be classified as an imperial topaz. It often appears at the ends of fashioned gems such as pear shaped or oval shaped gems. Otherwise it will have a yellowish orange body colour

Sherry Topaz / Precious Topaz
Sherry Topaz is often used to refer to Topaz that contain yellowish brown, brownish yellow and orange hues within them. This term is used because the colour of the stone resembles the colour of Sherry wine. Stones in this colour range are sometimes called precious topaz as well. The name is used to distinguish between citrine and smoky quartz which look similar and often times mistaken as Topaz.

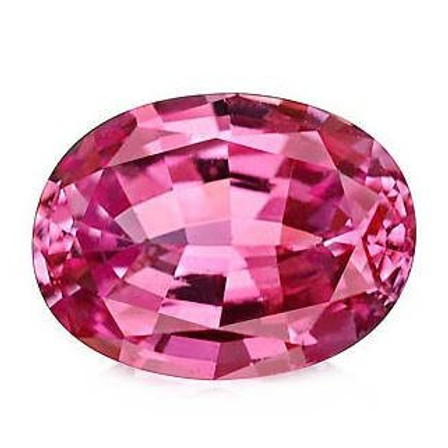
Pink Topaz / Rose Topaz
Pink Topaz, often known as Rose Topaz, is a naturally colour topaz found within Brazilian mines. It resembles a pink diamond or a bright pink sapphire, which people might mistake it for. It is less expensive than pink diamonds in generally and it is also readily available in large sizes compared to pink diamonds and pink sapphires.

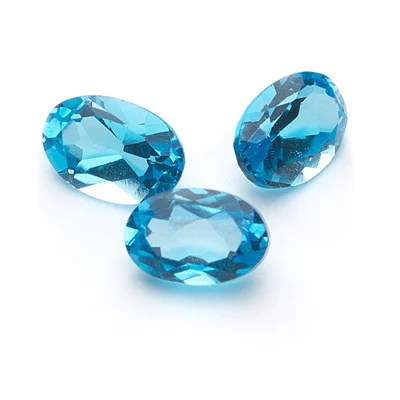
Sky Blue / Swiss Blue / London Blue Topaz
Contrary to popular believe, blue topaz are not naturally occurring topaz. The blue hue is achieved through treatment of the original gemstone. Therefore, supply for blue topaz can be easily generated and it is relatively cheap compared to the other stones. Different shades of blue have different trade names in this scenario. Sky Blue for aqua blue topaz, Swiss Blue for medium blue topaz and London Blue topaz for dark blue topaz

Clarity
Clarity of a gem is judged based off the gem’s opacity and how much inclusions does the gem contain. The assessment of clarity is often done thru eye clean and it follow the same grading as with diamonds. Inclusions within the gem affects the value of the gem. The more visible the inclusions are to the visible eye, the lower the value of the gem.

Topaz Gems are often inclusion-free. This is due to the nature of treatment being done to the gem to change their colour. Because of treatment, most stones will not contain inclusions. This is especially true when it comes to colourless, blue, yellow coloured topaz gems
Clarity Grades of Topaz
Clarity in transparent emeralds is assessed by naked eye only and at distance of about 40cm. Topaz are classified as type 1 stones. This means that they will almost always don’t have inclusions that are visible to the naked eye.
Cut
The shape of the Topaz crystal influences the finished stone’s shape and size. It is usually elongated or columnar thus it is often cut as long oval or pear shapes. If it has strong colour shades, it will be cut into emerald cut because that maximises the colour and retain the most weight.

But it is not only limited to just those 2 cuts. It can also cater to a large variety of shapes and cutting styles. It can come in all the gem shapes like Ovals, Pears, Rounds, Cushions, Marquise as well as designer cuts and fantasy shapes.
Fancy Cuts such as brilliant cuts with triangular facets, step cuts with parallel facets, and mixed cuts consisting of both are all common. Since there is an abundant supply of topaz, mainly blue topaz, it is often cut into specific and calibrated sizes for the usage of the mass consumer market and multi stone jewellery pieces.
Carat
Gemstones such as Topaz are denser than diamonds, therefore the carat weight for a gemstones differs from that of a diamond. Size of gemstones, including topaz, are measured by carat as well as their diameter in millimetres.
Topaz have a wide size range from a few points to hundreds of carats. Topaz in museums and private collections that weigh hundreds of carats, such as the ones in the Smithsonian and American Museum of Natural History. On the other end, smaller sized topaz gems are relatively inexpensive and easy to find. Prices tend to rise for gems that are above 10×8 mm in size.